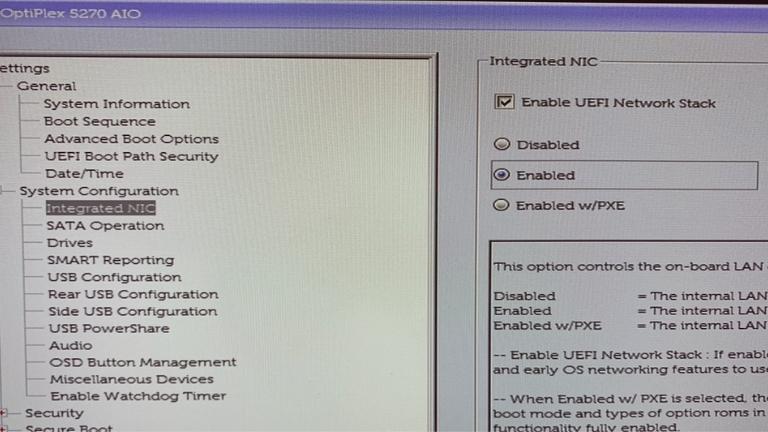
UEFI Network Stack BIOS is a firmware technology designed to enable the booting of operating systems on computers.
It is based on the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI), which has replaced the traditional BIOS firmware.
The UEFI Network Stack BIOS is a component of the UEFI specification that enables the booting of operating systems over a network.
In this article, we will explore the workings of UEFI Network Stack BIOS, its benefits, and how it operates.
What is UEFI?
UEFI, or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, is a firmware technology that offers a modern interface between the computer’s operating system and its hardware.
It serves as a replacement for the legacy BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) firmware that has been in use for several decades.
UEFI firmware provides several benefits over BIOS firmware, such as support for larger disk sizes, faster boot times, and compatibility with more advanced hardware.
Additionally, UEFI firmware is designed to be more secure than BIOS firmware, offering features such as secure boot and secure firmware updates.
Traditional BIOS vs. UEFI BIOS
For many years, traditional BIOS firmware has been used in computers, but it has several limitations.
These limitations include a lack of support for larger disks, slower boot times, and limited hardware support.
To overcome these limitations, UEFI firmware was introduced. UEFI firmware offers several advantages, including support for larger disks, faster boot times, and more advanced hardware support.
What is Network Booting?
Network booting is the process of starting up an operating system by using a network connection instead of a local storage device such as a hard drive.
To perform network booting, a network interface card (NIC) that supports network booting, a network boot server, and a boot image is required.
Network booting can be useful in situations where the computer’s hard drive is not available or not functioning properly.
UEFI Network Stack
The UEFI Network Stack is a component of the UEFI firmware that allows for network booting of the operating system.
This feature is used when the computer’s hard drive is not functioning properly or is not available.
With the UEFI Network Stack, the computer can boot from the network by utilizing the network interface card (NIC). The UEFI Network Stack supports various protocols, including PXE, TFTP, DHCP, and HTTP, which enables compatibility with various network environments.
How UEFI Network Stack Works
The UEFI Network Stack BIOS uses the network interface card (NIC) to communicate with the network boot server and obtain the boot image.
The UEFI Network Stack BIOS sends a request to the network boot server, which response by sending the boot image to the UEFI Network Stack BIOS.
The UEFI Network Stack BIOS then loads the boot image into the computer’s memory and executes it, allowing the operating system to be booted from the network.
This process enables the computer to boot even when the local storage device is not working properly or is unavailable.
Advantages of UEFI Network Stack
UEFI Network Stack BIOS offers several advantages over traditional firmware and booting methods. Some of the benefits of using UEFI Network Stack BIOS include:
- Faster boot times: UEFI Network Stack BIOS enables faster boot times than traditional BIOS firmware.
- Larger disk support: UEFI Network Stack BIOS can support disks larger than 2TB, which is not possible with traditional BIOS firmware.
- Secure boot: UEFI Network Stack BIOS supports secure boot, which ensures that the computer boots only from trusted sources.
- Network booting: UEFI Network Stack BIOS allows the operating system to be booted from the network, which is useful in environments where local storage devices are not available.
- Advanced hardware support: UEFI Network Stack BIOS supports more advanced hardware than traditional BIOS firmware.
Limitations of UEFI Network Stack
UEFI Network Stack BIOS also has some limitations that should be considered. Some of the limitations of UEFI Network Stack BIOS are:
- Network boot server required: UEFI Network Stack BIOS requires a network boot server to be available, which can be a challenge in some environments.
- Configuration complexity: UEFI Network Stack BIOS can be more complex to configure than traditional BIOS firmware, which can be a barrier for some users.
- Compatibility issues: Some hardware and network devices may not be compatible with UEFI Network Stack BIOS, which can limit its usability.
- Security concerns: While UEFI Network Stack BIOS supports secure boot, there are still potential security concerns associated with network booting, such as the risk of boot image tampering.
Overall, while UEFI Network Stack BIOS has several benefits, it is important to consider these limitations when deciding whether to use it in a particular environment.
Differences between UEFI Network Stack and PXE
PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) is a network booting protocol that is frequently used in conjunction with UEFI Network Stack BIOS. However, there are some distinctions between UEFI Network Stack and PXE:
- UEFI Network Stack is a component of the UEFI firmware, whereas PXE is a distinct protocol.
- While PXE only supports TFTP, UEFI Network Stack supports several protocols, including PXE, TFTP, DHCP, and HTTP.
- UEFI Network Stack BIOS provides a more advanced interface than PXE.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, UEFI Network Stack BIOS is a firmware technology that enables network booting of an operating system.
It offers several advantages over traditional firmware and booting methods, including faster boot times, larger disk support, secure boot, network booting, and advanced hardware support.
However, it also has some limitations, such as the need for a network boot server and proper configuration.